Mediterranean food and colorful variety
Rheumatology and nutritional medicine(18.03.2025) The inflammatory activity of chronic inflammatory diseases can be influenced by our dietary behavior. However, this cannot cure the disease, says one expert.
For rheumatologist and nutritionist Dr. Nora Bartholomä, head of rheumatological nutritional advice and the infusion outpatient clinic at the Department of Rheumatology at the Freiburg University Medical Centre, one thing is certain: "A balanced diet can influence the disease in the case of chronic inflammatory autoimmune diseases. But diet is an additional factor in treatment. It cannot cure the disease." In addition to diet, other factors also play a role in improving symptoms: Not smoking, getting plenty of exercise, avoiding obesity and excessive stress.
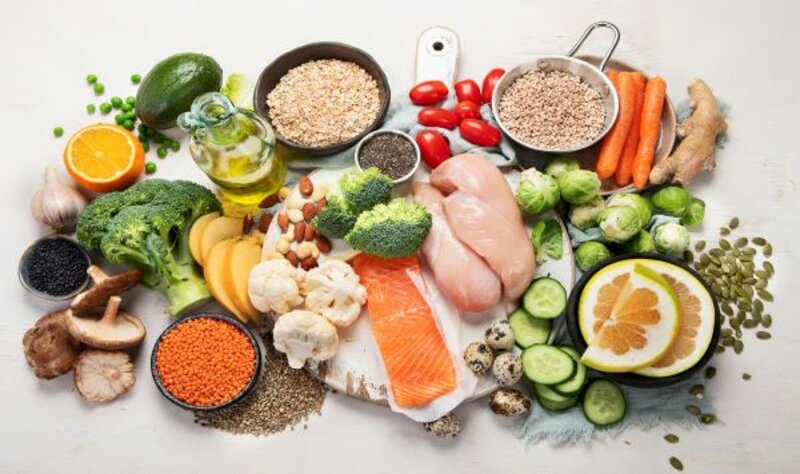

A large part of the diet should consist of vegetables and fruit. Protein-rich foods such as pulses and nuts as well as wholegrain products are also an important part of our daily meals. ©iStock
Eat anti-inflammatory foods: Green vegetables and oily fish
"Even though there is little research on how nutrition can help with rheumatoid arthritis, for example, there are forms of nutrition that can have an anti-inflammatory effect," says Bartholomä. Such a diet is based primarily on plant-based foods. Ideally, 75 percent of food should be of plant origin and only 25 percent of animal origin. According to some studies, omega-3 fatty acids, which are mainly found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel and herring, have an anti-inflammatory effect. Vegetables such as spinach, chard, leaf lettuce, watercress, zucchinis, chicory, broccoli, sugar snap peas, peas, kale, savoy cabbage, green beans and many others are particularly healthy. Vegetables are rich in vitamins and phytochemicals.
Good for the gut: fiber, fruit, healthy fats, proteins and nuts
Bartholomä adds that in addition to vegetables, fruit such as berries or citrus fruits are also an important part of the diet. A sufficient intake of fiber is particularly important in a balanced diet. These are food components that are not fully digested. "These fibers are very good for the intestines," says the expert. This is because a disturbed intestinal barrier can promote inflammation.
Proteins, which can also come from plant sources such as nuts, seeds and pulses, are filling and meet the protein requirements of the metabolism. Dairy products are allowed in moderation as long as they are well tolerated.
Stay away from too much salt, sugar and convenience foods
The nutritionist advises against highly processed foods such as ready-made products or soft drinks, sweet and savory snacks, which generally contain a lot of salt, sugar and saturated fatty acids and hardly any fiber. Red meat and highly processed sausages in particular are thought to contain pro-inflammatory substances and also increase the risk of some diseases, particularly bowel cancer. "These foods should only be consumed occasionally," says Bartholomä.
The DGE's nutritional circle can be implemented as part of a Mediterranean diet
The German Nutrition Society (DGE ) has published updated dietary recommendations for healthy adults in 2024. The recommended proportions of different food groups are visualized very clearly in the so-called nutrition circle. Plant-based foods are at the forefront, with nuts and pulses also having their place. Animal products only have a small place in the nutrition circle. When choosing drinks, the focus is on water and unsweetened teas. "The DGE's recommendations ultimately represent a kind of 'optimal diet' and take into account sustainability aspects as well as an adequate supply of nutrients," says Bartholomä.
Mediterranean diet also for inflammatory rheumatic diseases
In practical terms, the DGE recommendations can be implemented as part of a "Mediterranean diet", as the data situation is best for this: "In the case of inflammatory rheumatic diseases, a clear recommendation can be made for the Mediterranean diet. If you consciously avoid disease-promoting foods, you can influence inflammatory processes," explains the expert. It is important to maintain a healthy diet in the long term - "although occasional outliers are part of this - it is not about problematizing enjoyment". In individual cases, nutritional advice can help to determine together which changes in eating habits might be useful. Bartholomä recommends: "If possible, cook a varied diet with fresh food and avoid ready-made meals." The use of frozen vegetables is also permitted. It is helpful to follow the so-called Mediterranean diet.
10 tips for an anti-inflammatory diet
- Drink around 1.5 liters of water or other calorie-free drinks such as unsweetened tea every day. Sweetened and alcoholic drinks should be exceptions.
- Eat at least five portions of fruit and vegetables every day. They provide plenty of vitamins, minerals, fiber and phytochemicals.
- When it comes to cereal products such as bread, pasta, rice and flour, whole grains are the best choice for your health. Whole grain foods are more filling and contain more vitamins and minerals than white flour products.
- Pulses such as peas, beans and lentils are rich in protein, vitamins, minerals, fiber and phytochemicals. Nuts also provide useful fatty acids. For example, eat pulses once a week and a small handful of nuts every day.
- Vegetable oils are rich in essential fatty acids and vitamin E. Walnut, linseed, rapeseed and olive oil, for example, are recommended.
- Milk and dairy products provide protein, calcium, vitamin B2 and iodine and support bone health. With plant-based milk alternatives, attention should be paid to the supply of calcium in particular.
- Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel and herring provide valuable omega-3 fatty acids. Sea fish also contains iodine. Fish should be eaten once or twice a week.
- Take your time when eating and allow yourself breaks. Eating slowly and consciously promotes a feeling of fullness. Eating together is also good for you.
- Replace salt with herbs for seasoning.
- In addition to a healthy diet, make sure you get enough physical activity. Sleep regularly, refrain from smoking and aim for a normal body weight.
More interesting articles
Medical Center - University of Freiburg
Central InformationPhone: 0761 270-0
info@uniklinik-freiburg.de
Corporate Communications
Breisacher Straße 15379110 Freiburg
Phone: 0761 270-84830
kommunikation@uniklinik-freiburg.de