Key player found in viral myocarditis
Heart muscle inflammation following viral infection can impair heart function in the long term / Freiburg researchers now show that a specific immune cell receptor is crucial for virus elimination / New therapeutic approach possible
A serious consequence of a viral infection is inflammation of the heart muscle. This can impair heart function in the long term. In a recent study, researchers from the Faculty of Medicine - University of Freiburg have discovered a new approach to treating heart muscle inflammation, also known as myocarditis.Using an animal model, the research team showed that the immune cell receptor GPR15 is crucial in combating viruses in heart tissue. If these receptors are not present, virus elimination is slower and consequential damage can occur. The results were published on December 27, 2023 in the journal Nature Cardiovascular Research .
"myocarditis progresses very differently in different patients. We have now been able to identify a central player in the immune defense that has a central influence on the course of viral elimination. If we were able to intervene here in a targeted manner, we could significantly improve the chances of recovery," says study leader Dr. Diana Lindner, who heads the Molecular Cardiology research group at the Department of Cardiology and Angiology of the University Heart Center - University of Freiburg.
Missing receptor slows down the immune response
The study was carried out as part of the Collaborative Research Center 1425 "The Heterocellular Nature of Cardiac Lesions" at the University of Freiburg. It shows that the immune receptor GPR15 plays a key role in the recruitment of immune T cells into the inflamed heart tissue. In the mouse model, GPR15 deficiency led to delayed clearance of the viruses, which in turn led to negative changes in the heart muscle and impaired heart function. A slowed and subsequently prolonged inflammatory response was measurable.
Myocarditis - medication and rest
The treatment of myocarditis varies depending on the severity and usually involves medication to stabilize heart function and contain the inflammation. Patients should avoid physical exertion and take it easy to avoid long-term damage. The therapeutic approaches range from immunomodulation to supportive measures to maintain heart function, depending on the individual dynamics of the disease.
Original title of the study: GPR15-mediated T cell recruitment during acute viral myocarditis facilitated virus elimination and improved outcome
DOI: 10.1038/s44161-023-00401-z
Link to the study:https://rdcu.be/duzAK
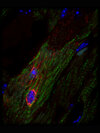
Caption: The heart muscle cell (cardiomyocyte) is easily recognizable due to its characteristic transverse stiffening (green). The viral infection of this cell is shown by the red-stained viral RNA.
Image source: Medical Center - University of Freiburg (Hanna Wolf, AG Lindner, Department of Cardiology and Angiology)
Back
Medical Center - University of Freiburg
Central Information
Phone: 0761 270-0
info@uniklinik-freiburg.de
For press inquiries:
Corporate Communications
Breisacher Straße 153
79110 Freiburg
Phone: 0761 270-84830
kommunikation@uniklinik-freiburg.de