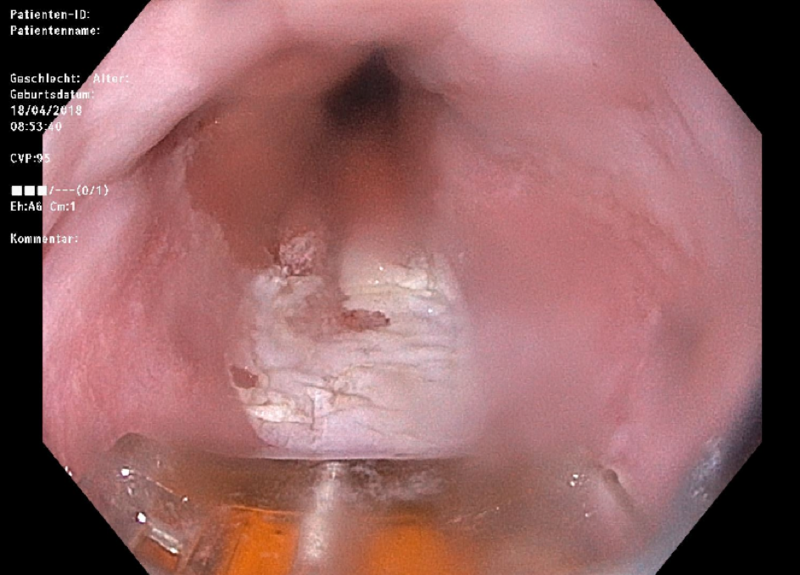
Scabbing of the Barrett's mucosa (radiofrequency ablation)
In the case of chronic reflux, a reflux of stomach acid into the oesophagus, the mucous membrane in the oesophagus can change pathologically over time due to inflammation. It then resembles the mucous membrane in the small intestine. This change, known as Barrett's mucosa, can be removed using a new endoscopic treatment, radiofrequency ablation. The treatment takes 30 to 60 minutes and is carried out as part of a gastroscopy. An inpatient stay of three to four days is the rule.
A balloon equipped with electrodes on the surface is inflated in the oesophagus under endoscopic control and touches the Barrett's mucosa. The water in the cells of the mucous membrane is heated to boiling point by applying a controlled radio frequency current via a generator. The Barrett's mucosa then scabs over, deeper layers of tissue are not affected and the function of the oesophagus remains intact. After treatment, the Barrett's mucosa is replaced by the normal, upper cell layer of the esophageal mucosa.