Brain tumors
Tumors of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) occur rarely in adults, they account for about 10 new cases per year per 100,000 adults. In childhood, brain tumors are more frequent and after leukemia responsible for every second of all cancer deaths. As in all organs tumors in the brain may be benign as well as malignant. Benign and malignant tumors have different characteristics.
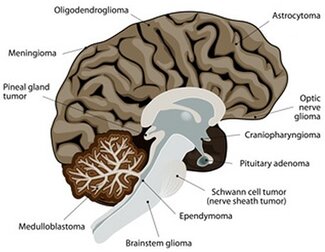
Brain tumors are classified according to cell type and tissue of origin. About 45 percent represent Gliomas arising from the supporting tissue. However, relatively rare are tumors of the meninges (meningiomas), tumors of the pituitary gland (pituitary adenoma), tumors of the cranial nerves or lymphoma. More often metastases, secondary brain tumors, arise than primary brain tumors. More than 20 percent of patients with a malignancy develop a metastasis in the brain during the course of their disease. The most common cerebral metastases arise from lung cancer (30-60 percent), breast cancer (15-40 percent) and skin cancer (melanoma, 10 percent).
The adequate treatment of a tumor can be very different depending on its characteristics and its localization. In case of a benign tumor an operation can lead to a permanent and complete cure, in case of a malignant tumor on the other hand the multimodal treatment aims at reducing the tumor mass and preventing the progressive growth of the tumor.
The most common primary brain tumors
Contact

Prof. Dr. Marcia Machein
Head consultation hours
for tumor patients
Consultation hours for tumor patients