Borna Disease Virus
Borna disease virus (BDV) is an enveloped virus with an RNA genome of negative polarity which replicates in the nucleus of the infected cell. BDV can persistently infect neurons of the central nervous system without causing general cell death, reflecting a unique adaptation to the brain. This adaptation of BDV is accompanied by subtle consequences for infected neurons, including changes in the neuronal and synaptic plasticity and epigenetic alterations. However, BDV can also cause an immune-mediated pathology of the brain in various animal species; however, there is no evidence so far that BDV can also infect humans. Intriguingly, zoonotic transmission of a related BDV, the Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus, from squirrels to humans was recently reported to cause fatal encephalitis. The requirements of these newly identified bornaviruses to cross the species barrier are currently studied in a newly formed Zoonotic Bornavirus Consortium (ZooBoCo) funded by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung.
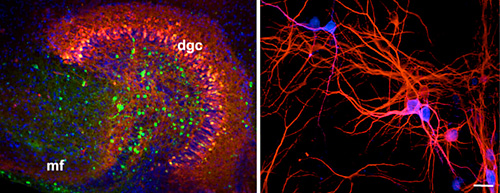
Infection of hippocampus slice cultures with Borna Disease Virus (BDV).
Left panel: Hippocampus slice cultures obtained from a newborn Lewis rat was infected with BDV and stained 2 weeks after infection for BDV (green), calbindin (red), which is a maker for dentate granule cells.. mf, mossy fiber, dgc, dentate granule cells.
Right panel: Dissociated primary neuronal cultures were obtained from the cortex of newborn Lewis rats. They were infected with BDV for 1 week and subjected to immunofluorescence analysis by using specific antibodies against BDV (blue) and Map2 (red), a specific marker of neurons. Bar 40 μm.
Publications:
- Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Jun;20(6):651.doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30379-0.
Are Human Borna Disease Virus 1 Infections Zoonotic and Fatal? - Authors' Reply
Dennis Rubbenstroth, Hans H Niller, Klemens Angstwurm, Martin Schwemmle, Martin Beer
- THELANCETID-D-19-00544 S1473-3099(19) 30546-8Published:January 07, 2020
Zoonotic spillover infections with Borna disease virus 1 leading to fatal human encephalitis, 1999–2019: an epidemiological investigation
Hans Helmut Niller, Klemens Angstwurm, Dennis Rubbenstroth, Kore Schlottau, Arnt Ebinger, Sebastian Giese, Silke Wunderlich, Bernhard Banas, Leonie F Forth, Donata Hoffmann, Dirk Höper, Martin Schwemmle, Dennis Tappe, Jonas Schmidt-Chanasit, Daniel Nobach, Christiane Herden, Christoph Brochhausen, Natalia Velez-Char, Andreas Mamilos, Kirsten Utpatel, Matthias Evert, Saida Zoubaa, Markus J Riemenschneider, Viktoria Ruf, Jochen Herms, Georg Rieder, Mario Errath, Kaspar Matiasek, Jürgen Schlegel, Friederike Liesche-Starnecker, Bernhard Neumann, Kornelius Fuchs, Ralf A Linker, Bernd Salzberger, Tobias Freilinger, Lisa Gartner, Jürgen J Wenzel, Udo Reischl, Wolfgang Jilg, André Gessner, Jonathan Jantsch, Martin Beer*, Barbara Schmidt*Hans Helmut Niller, MD †
- Sci Rep. 9 (1), 20154 2019 Dec 27
Low Prevalence of Borna Disease Virus 1 (BoDV-1) IgG Antibodies in Humans From Areas Endemic for Animal Borna Disease of Southern Germany
Dennis Tappe , Christina Frank, Ruth Offergeld, Christiane Wagner-Wiening, Klaus Stark, Dennis Rubbenstroth, Sebastian Giese, Erik Lattwein, Martin Schwemmle, Martin Beer, Jonas Schmidt-Chanasit, Hendrik Wilking
- PLoS Pathog. 2019 Aug 1;15(8):e1007873. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007873. eCollection 2019 Aug.
Human bornavirus research: Back on track!
Rubbenstroth D, Schlottau K, Schwemmle M, Rissland J, Beer M.
- N Engl J Med. 2018 Oct 4;379(14):1377-1379. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1803115.
Fatal Encephalitic Borna Disease Virus 1 in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients.
Schlottau K, Forth L, Angstwurm K, Höper D, Zecher D, Liesche F, Hoffmann B, Kegel V, Seehofer D, Platen S, Salzberger B, Liebert UG, Niller HH, Schmidt B, Matiasek K, Riemenschneider MJ, Brochhausen C, Banas B, Renders L, Moog P, Wunderlich S, Seifert CL, Barreiros A, Rahmel A, Weiss J, Tappe D, Herden C, Schmidt-Chanasit J, Schwemmle M, Rubbenstroth D, Schlegel J, Pietsch C, Hoffmann D, Jantsch J, Beer M.
- J Virol 79: 11716-23 (2005)
Borna disease virus replication in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures from rats results in selective damage of dentate granule cells
Mayer, D., H. Fischer, U. Schneider, B. Heimrich, and M. Schwemmle.
- Proteomics 5: 483-7 (2005)
Isolation of viral ribonucleoprotein complexes from infected cells by tandem affinity purification
Mayer, D., S. Baginsky, and M. Schwemmle.
- Virus Res 111: 224-34 (2005)
Borna disease virus interference with neuronal plasticity
Gonzalez-Dunia, D., R. Volmer, D. Mayer, and M. Schwemmle.
- J Virol 79: 11716-23 (2005)
Borna disease virus replication in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures from rats results in selective damage of dentate granule cells
Mayer, D., H. Fischer, U. Schneider, B. Heimrich, and M. Schwemmle.
- Proteomics 5: 483-7 (2005)
Isolation of viral ribonucleoprotein complexes from infected cells by tandem affinity purification
Mayer, D., S. Baginsky, and M. Schwemmle.
- Virus Res 111: 224-34 (2005)
Borna disease virus interference with neuronal plasticity
Gonzalez-Dunia, D., R. Volmer, D. Mayer, and M. Schwemmle.
- Virus Res. 2005 Aug;111(2):224-34.
Borna disease virus interference with neuronal plasticity.
Gonzalez-Dunia D1, Volmer R, Mayer D, Schwemmle M.
- J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 31;279(53):55290-6. Epub 2004 Oct 27.
Overlap of interaction domains indicates a central role of the P protein in assembly and regulation of the Borna disease virus polymerase complex.
Schneider U, Blechschmidt K, Schwemmle M, Staeheli P.
- Mol Divers. 2004;8(3):247-50.
The use of peptide arrays for the characterization of monospecific antibody repertoires from polyclonal sera of psychiatric patients suspected of infection by Borna Disease Virus.
Schwemmle M, Billich C.
- J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(21):11781-9.
Active borna disease virus polymerase complex requires a distinct nucleoprotein-to-phosphoprotein ratio but no viral X protein.
Schneider U, Naegele M, Staeheli P, Schwemmle M.
- J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(7):4283-90.
Selective virus resistance conferred by expression of Borna disease virus nucleocapsid components.
Geib T, Sauder C, Venturelli S, Hässler C, Staeheli P, Schwemmle M.
- Arch Virol. 2003 Jan;148(1):45-63.
Identification of differentially expressed genes in brains of newborn Borna disease virus-infected rats in the absence of inflammation.
Jehle C, Herpfer I, Rauer M, Schwemmle M, Sauder C.
- Biol Psychiatry. 2002 Jun 15;51(12):979-87.
High-avidity human serum antibodies recognizing linear epitopes of Borna disease virus proteins.
Billich C, Sauder C, Frank R, Herzog S, Bechter K, Takahashi K, Peters H, Staeheli P, Schwemmle M.
- Lancet Infect Dis. 2001 Aug;1(1):46-52.
Borna disease virus infection in psychiatric patients: are we on the right track?
Schwemmle M.
- J Gen Virol. 2001 Nov;82(Pt 11):2681-90.
Conservation of coding potential and terminal sequences in four different isolates of Borna disease virus.
Pleschka S, Staeheli P, Kolodziejek J, Richt JA, Nowotny N, Schwemmle M.
- J Gen Virol. 2000 Sep;81(Pt 9):2123-35.
Epidemiology of Borna disease virus.
Staeheli P, Sauder C, Hausmann J, Ehrensperger F, Schwemmle M.
- J Virol. 2000 Sep;74(17):7878-83.
Sequence variability of Borna disease virus: resistance to superinfection may contribute to high genome stability in persistently infected cells.
Formella S, Jehle C, Sauder C, Staeheli P, Schwemmle M.
- J Gen Virol. 2000 Aug;81(Pt 8):1947-54.
Authentic Borna disease virus transcripts are spliced less efficiently than cDNA-derived viral RNAs.
Jehle C, Lipkin WI, Staeheli P, Marion RM, Schwemmle M.
- J Virol. 2000 Jun;74(12):5655-8.
Isolation and characterization of a new subtype of Borna disease virus.
Nowotny N, Kolodziejek J, Jehle CO, Suchy A, Staeheli P, Schwemmle M.
- Lancet. 1999 Dec 4;354(9194):1973-4.
Sequence similarities between human bornavirus isolates and laboratory strains question human origin.
Schwemmle M, Jehle C, Formella S, Staeheli P.
- Arch Virol. 1999;144(4):835-40.
Progress and controversy in Bornavirus research: a meeting report.
Schwemmle M.
- J Gen Virol. 1999 Jan;80 ( Pt 1):97-100.
Characterization of the major nuclear localization signal of the Borna disease virus phosphoprotein.
Schwemmle M, Jehle C, Shoemaker T, Lipkin WI.
- J Biol Chem. 1998 Apr 10;273(15):9007-12.
Interactions of the borna disease virus P, N, and X proteins and their functional implications.
Schwemmle M, Salvatore M, Shi L, Richt J, Lee CH, Lipkin WI.
- J Virol. 1998 May;72(5):4379-86.
Borna disease virus-induced neurological disorder in mice: infection of neonates results in immunopathology.
Hallensleben W, Schwemmle M, Hausmann J, Stitz L, Volk B, Pagenstecher A, Staeheli P.
- J Virol. 1997 Nov;71(11):8940-5.
Implication of a cis-acting element in the cytoplasmic accumulation of unspliced Borna disease virus RNAs.
Schneider PA, Schwemmle M, Lipkin WI.
- J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 29;272(35):21818-23.
Borna disease virus P-protein is phosphorylated by protein kinase Cepsilon and casein kinase II.
Schwemmle M, De B, Shi L, Banerjee A, Lipkin WI.
- Lancet. 1997 Jun 21;349(9068):1813-4.
Borna disease virus in brains of North American and European people with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Bornavirus Study Group.
Salvatore M, Morzunov S, Schwemmle M, Lipkin WI.

Head:
Prof. Dr. med. Hartmut Hengel
hartmut.hengel@uniklinik-freiburg.de
| Secretary | Administration | Information desk |
|---|---|---|
Kristina Gendrisch Telefon: 0761 270-83480 Telefax: 0761 270-83479 | Gudrun Simpson Telefon: 0761 270-83711 Telefax: 0761 270-83703 | Jutta Schneeberger Telefon: 0761 270-83700 Telefax: 0761 270-83703 |