AG Dr. Badr
Dr. med. Mohamed Tarek Badr
| Telefon Büro | +49 761 270-83685 |
|---|---|
| Fax | +49 761 270-83703 |
| mohamed.tarek.badr@uniklinik-freiburg.de |
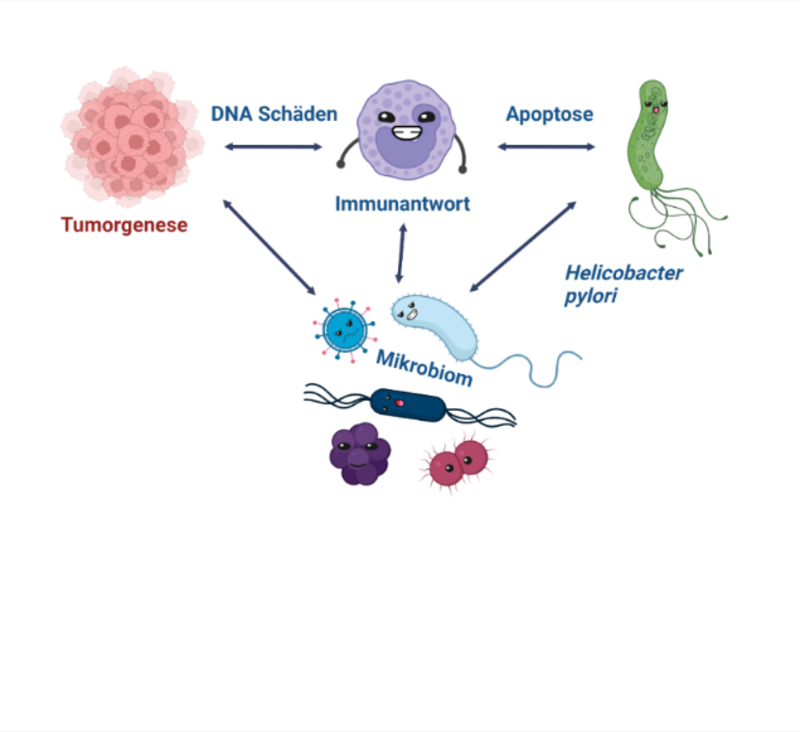
Pathogen-Mikrobiom Interaktion im Zusammenhang mit humaner Immunantwort während der Infektion und Kolonisation mit Helicobacter pylori (PREDICT-HP)
Details zum Ablauf der Studie:
Für die Studie erfolgt ein Aufklärungsgespräch mit anschließender Blutentnahme im Institut für medizinische Mikrobiologie und Hygiene, ebenso muss eine Stuhlprobe abgegeben werden. Hierfür werden alle Utensilien in einem Kit bereitgestellt, sodass die Probenentnahme flexibel gestaltet werden kann. Die Stuhlproben müssen ebenfalls im Institut für medizinische Mikrobiologie und Hygiene abgeben werden. Darüber hinaus gibt es keine Folgetermine.
Sind Sie interessiert?
Wir suchen Personen im Alter zwischen 18-65 Jahren, um die Pathogen-Mikrobiom Interaktion im Zusammenhang mit der menschlichen Immunantwort während der Kolonisation mit Helicobacter pylori zu untersuchen. H. pylori ist ein Bakterium, das die Magenschleimhaut von etwa der Hälfte der Menschen weltweit besiedelt. In Westeuropa ist dieser Anteil in den letzten Jahrzehnten auf etwa 20-30 % gesunken. Diese Besiedlung ist in den meisten Fällen eine harmlose Kolonisation, welche sogar mit gewissen Vorteilen verknüpft sein kann. Lediglich bei einem sehr kleinen Anteil der besiedelten Menschen kommt es darüber hinaus jedoch zu Erkrankungen: Magenschleimhautentzündungen, Magengeschwüre, sowie Magenkrebs sind mit einer Besiedlung durch H. pylori assoziiert. Es ist bislang noch unverstanden, weshalb die Kolonisation bei verschiedenen Menschen so unterschiedlich verläuft. Durch „multi-omics“ Machine Learning Ansätze wollen wir hier diese Frage angehen.
Voraussetzungen für die Teilnahme:
- Alter: 18 bis 65 Jahre
- Keine Schwangerschaft
- Kein Diabetes
- Keine akuten/chronischen Krankheiten/Beschwerden des Verdauungssystems
- Keine Blutgerinnungsstörungen
- Keine Antibiotika ≤ 4 Wochen vor Studienstart
- Keine starke Diarrhoe ≤ 4 Wochen vor Studienstart
Kontakt:
Möchten Sie an der Studie teilnehmen oder weitere Informationen erhalten? Dann nehmen Sie Kontakt mit uns auf:
E-Mail:
anne.sophie.lichtenegger@uniklinik-freiburg.de
mohamed.tarek.badr@uniklinik-freiburg.de
Tel.: 0761 203-6585
Who is who?
| Name | Position | Telefon | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dr. med. Mohamed Tarek Badr | AG-Leiter | +49 761 270 83685 | mohamed.tarek.badr@uniklinik-freiburg.de |
| Uzochukwu Ukachukwu | Biol. Doktorand | +49 761 270 83685 | uzochukwu.gospel.ukachukwu@uniklinik-freiburg.de |
| Ivan Potereba | Biol. Doktorand | +49 761 270 83685 | ivan.potereba@uniklinik-freiburg.de |
CV
| 09/2007-02/2015 | Studium der Humanmedizin, Mansoura Universität Ägypten |
| 03/2014-02/2015 | PJ im Mansoura Allgemeinkrankenhaus |
| 03/2015-04/2015 | Allgemeinmediziner im Ministerium für Gesundheit und Bevölkerung, Daqahliyya Ägypten |
| 08/2015-02/2018 | Institut für experimentelle Dermatologie, Lübeck |
| 03/2018 | Promotion "Identyfying mitochondrial functions modulators in Alzheimer´s disease" Institut für experimentelle Dermatologie, Lübeck |
| Seit 02/2018 | Arzt in Weiterbildung, Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie und Hygiene, Universität Freiburg |
Clinical metagenomics Application of high-throughput techniques in clinical microbiology and recent advances in next generation sequencing (NGS) techniques have enabled us to explore a wide variety of pathogens in a broader and more efficient manner, and illustrated the complexity of the microbial communities that inhabit the human body. We are interested in harnessing these advances and implementing high-throughput techniques in infection diagnosis and treatment and study the role of the human microbiome in disease pathogenesis. |
Analysis of high-throughput data We use high-throughput sequencing technologies in infection models to study several host-pathogen interactions. By using genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic analyses we hope to understand the role of the apoptosis system in infection-induced tumorigenesis and host microbiome modulation. |
| Mitochondrial dynamics and functions in host-pathogen interactions |
Helicobacter pylori infections |
