Preclinical Imaging Research Center and Core Facility

The main focus of AMIR is multimodal imaging for pre-clinical and translational research. Our work is dedicated to the fusion of cellular research and clinical projects in development and implementation of novel and advanced techniques for small animal imaging. Modalities used include in vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), small animal Ultrasound, optical imaging and µCT with a focus on photon counting techniques.
AMIR-CF is a certified Core Facility and co-funded by the Medical Faculty of the University Freiburg. It is furthermore registered at the RIsources portal of the DFG. The goal of AMIR-CF is to provide innovative preclinical imaging technology and research tools for our partners in the University and beyond. Usage of our facilites is possible in service- and in self-responsible- operation mode.
Equipment of the Research Group AMIR
The small animal imaging research group AMIR currently runs 3 dedicated in vivo MRI systems, an NMR spectrometer with in vitro high resolution imaging option, a mouse/rat Ultrasound, an in vivo small animal µCT, and an in vitro photon counting µCT. In addtion a small histology lab with a cryotome and microscopy is availabe. These research facilities are located in the basement of the Neuro Center and the 3rd floor of the IMITATE research building.
All systems are in principle accessible for external researchers as well via the Core Facility AMIR-CF.

SFB 1479
The Collaborative Research Center (CRC) 1479 “Oncogene-driven immune escape” is a research consortium of clinical and basic tumor biologists and immunologist. Our CRC builds on the scientific hypothesis that oncogenic signalling and immune escape mechanisms are closely connected. This concept implies that targeting of oncogene-driven immune evasion could take treatment beyond palliative therapy towards cures for different types of cancer.
DKTK
The Research Program Translational Cancer Research , is based on the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) within the National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT) Heidelberg and has its focus on the transfer of approaches in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cancer to clinical application.

SFB 1425 Make better scars!
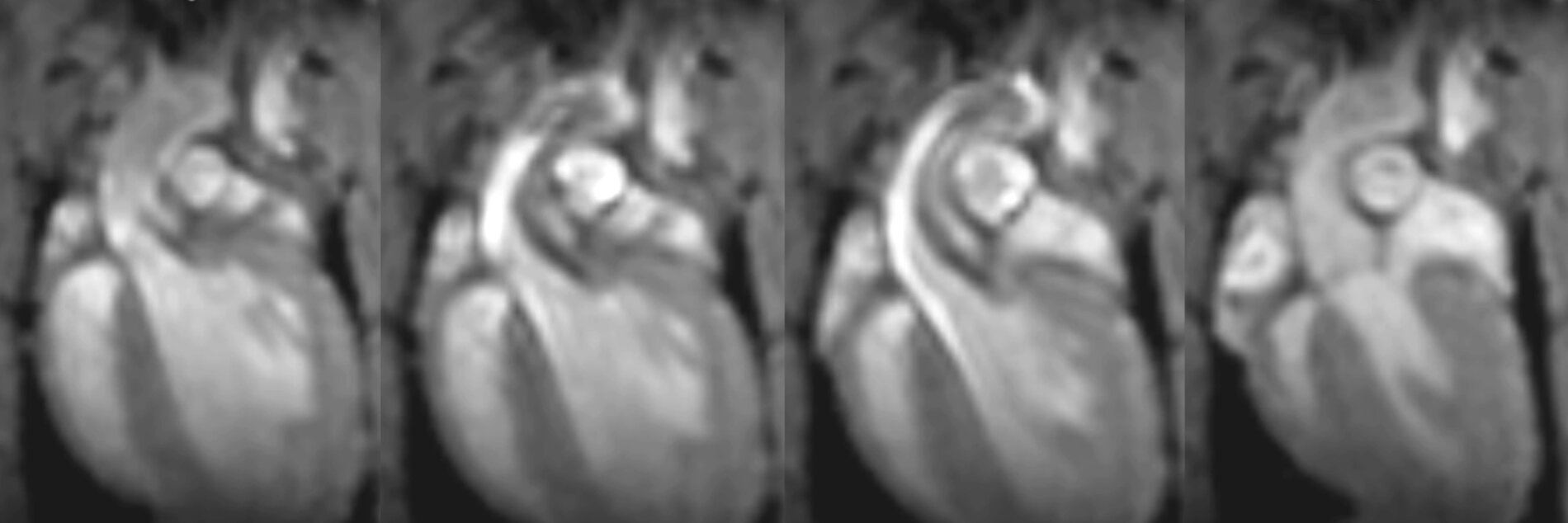
Traditionally, heart research has strongly focussed on cardiac myocytes: they are the motors underlying cardiac pumping, driving classic clinical read-outs such as blood pressure or ECG. Cardiomyocytes occupy about two thirds of cardiac muscle volume.Our knowledge of cellular identities of non-myocytes, the mechanisms and relevance of their interactions, and the use of this knowledge to steer repair processes, is still in its infancy. These areas will be investigated by the CRC 1425, with the long-term aim of developing new methods for diagnosis and therapy of heart disease. In doing so, the CRC is not primarily targeting scar prevention or retransformation into functional muscle tissue, but rather pursuing a new and complementary approach, working with nature’s own repair processes ‘to make better scars’.
SFB 850 (2010 -2022)
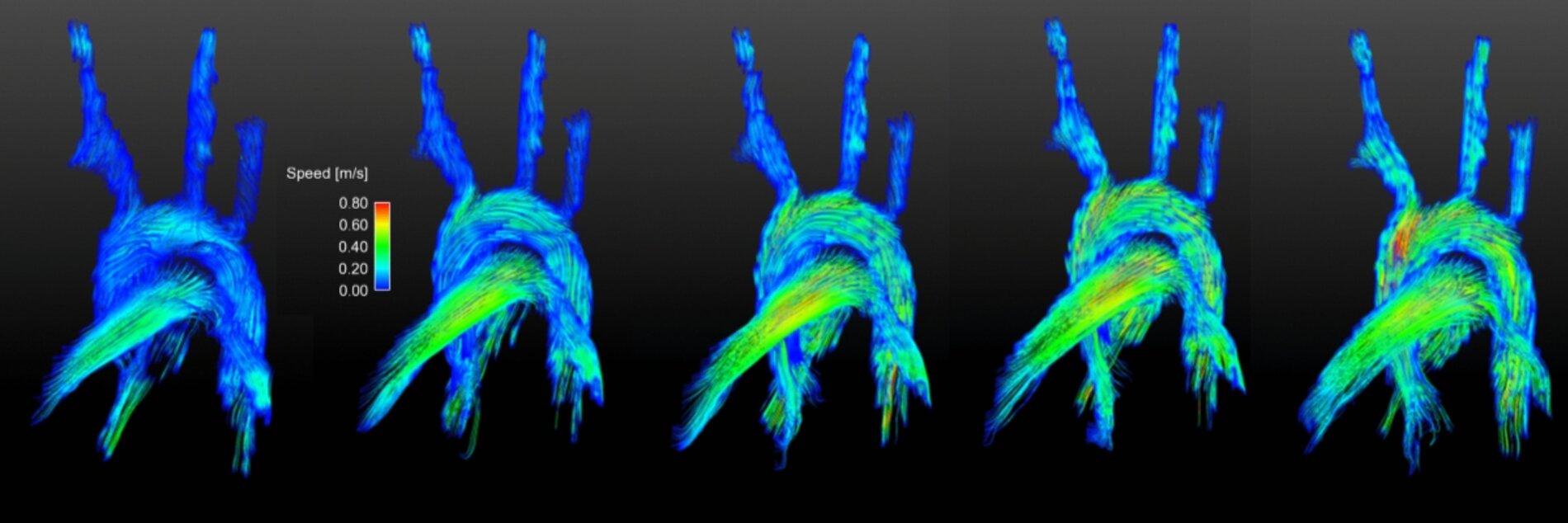
Within the SFB 850 AMIR runs the core facility project Z2 “Imaging” in cooperation with the Dept. of Haematology and Oncology and the Dept. of Nuclearmedicine. It offers small animal imaging support and advice employing bioluminescence, micro PET and MRI techniques.

NANOTRANSMED
NANOTRANSMED is a European project, led by a french-german-swiss consortium and cofinanced by the INTERREG VA Upper Rhine Programme. NANOTRANSMED enables French, German and Swiss scientists to develop together applications and innovations in nanomedicine. On the basis of new approaches, made possible by the use of nano-objects (probes, smart implants …), it is now possible to create innovative and efficient solutions meeting major issues regarding patients’ care. The NANOTRANSMED consortium focuses in particular on issues concerning early, reliable and fast diagnosis but also personalized treatment of diseases such as cancers and inflammation as well as issues regarding nosocomial infections contracted by 5% of hospitalized patients.
BrainLinks-BrainTools
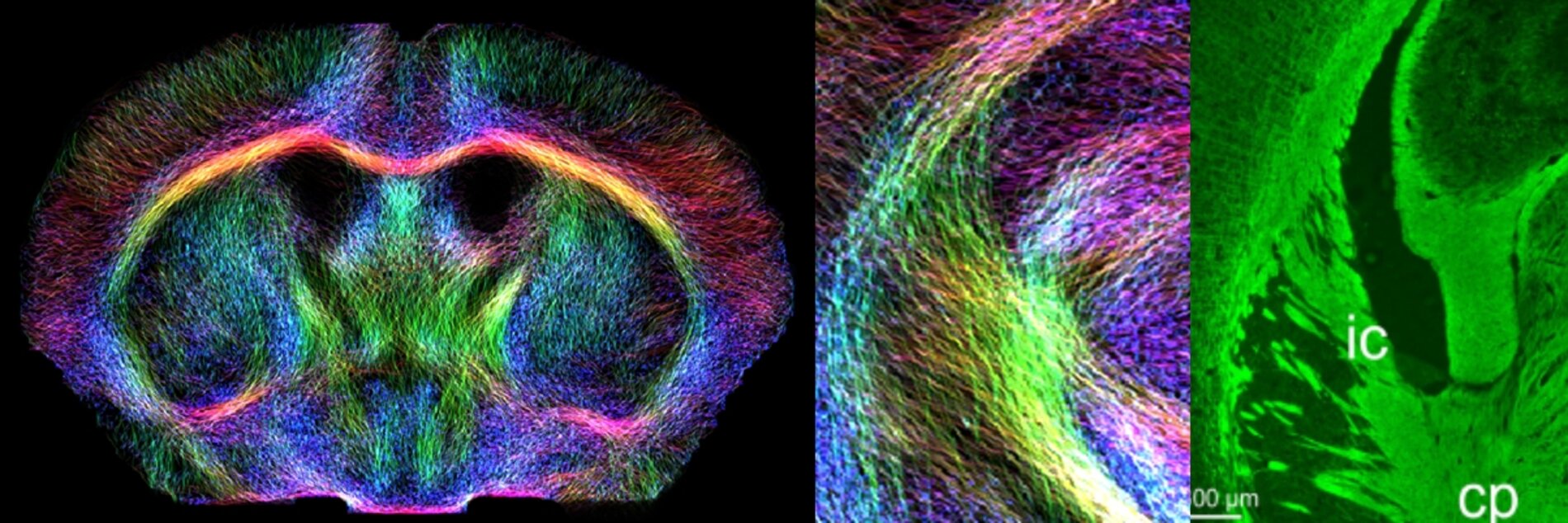
BrainLinks-BrainTools aims to develop medical technology that directly interacts with the nervous system. For this purpose, it unites the life sciences, engineering, and clinical applications. BrainLinks-BrainTools is a Cluster of Excellence, funded since 2012 within the German Excellence Initiative

ENCITE
Cell therapy can be defined as the transplantation of living cells for the treatment of medical disorders. The development of relevant imaging tools will lead to a better understanding of how cell therapy works, the possibility of response monitoring in patients, and sufficient safety of the treatment.. ENCITE will provide tools to allow this by developing; • New imaging methods to improve the spatio-temporal tracking of labelled cells • Dual- and multimodality imaging procedures to cross-validate each individual approach • New contrast agents and procedures that will improve the sensitivity and specificity of cellular labelling The tools and methodologies developed will be validated in 5 key disease areas; Neurological, Cardiovascular, Musculoskeletal, Diabetes and Cancer.
apl. Prof. Dr. Dominik von Elverfeldt
Head of AMIR
Tel.: +49 761 270-38320
E-Mail: dominik.elverfeldt@uniklinik-freiburg.de
University Medical Center Freiburg
Dept. of Radiology · Medical Physics
Killianstr. 5a
79106 Freiburg